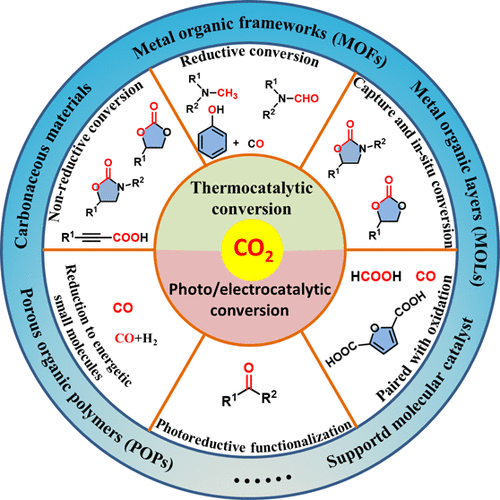
CO2 accumulation and its detrimental environmental impacts have become issues of public concern. To address the carbon emission issues, various strategies have been proposed, among which carbon capture and utilization (CCU), one of the negative carbon technologies, is regarded as an important initiative. In particular, converting such captured CO2 to valuable products without desorption can avoid energy consumption in CO2 desorption. Furthermore, the captured CO2 can be considered to be the activated CO2 species and thus promotes the subsequent transformation under mild conditions.
CO2 is a thermodynamically stable molecule with a standard formation enthalpy of 393.5 kJ mol–1. Simultaneously, the linear symmetric structure makes CO2 a kinetically inert molecule. The above features imply that the CO2 transformation relies on efficient CO2 activation and high energy input (from the substrate with high free energy or external light and/or electrical energy). Accordingly, the activation of CO2 through thermo-, photo-, or electrocatalytic processes is a prerequisite to CO2 valorization.
Recently, Liang-Nian He’s group introduced the activation mechanism of CO2 and substrates, as well as the rational design of nanocatalytic materials based on conversion strategies. They demonstrated the research ideas and processes of using molecular engineering technology to reasonably design nanomaterials and achieve the transition from molecular catalysis to heterogeneous catalysis, which helps to comprehensively understand the role of nanocatalytic materials in CO2 resource utilization, At the same time, it provides beneficial insights for the development of new CO2 conversion strategies based on rational design of nanomaterials. Relevant achievements were published in Acc. Chem. Res., 2023, DOI: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00316.