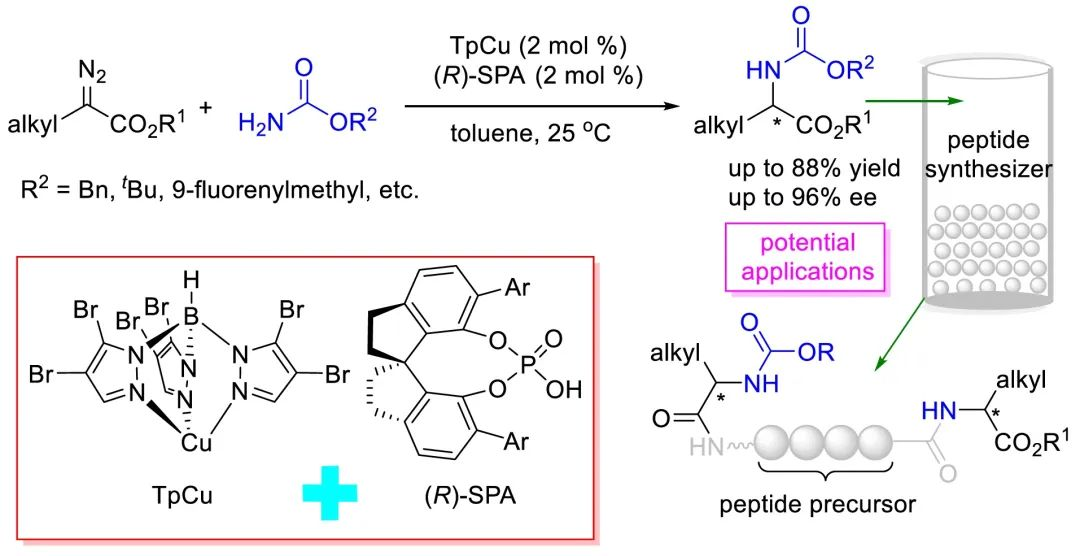
Peptides have found numerous biological applications. For example, peptide-based vaccines have been developed for various diseases, including influenza, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. Synthetic peptides, especially those containing fewer than 50 amino acids, have been attracting increasing attention in recent years. The rising demand for artificial peptides in general, and for peptides with unnatural amino acids in particular, has increased the importance of developing methods for selective, highly efficient synthesis of carbamate-protected unnatural amino esters. One straightforward method for synthesizing such compounds in an optically active form involves catalytic asymmetric insertion of carbenes into the N–H bonds of carbamates. To date, only carbenes derived from α-aryl- and α-alkenyl-α-diazoacetates (8,9) have shown high enantioselectivity in N–H bond insertion reactions with carbamates.
Recently, Shou-fei Zhu’ group developed a method for highly enantioselective N–H bond insertion reactions of α-alkyl-α-diazoacetates and various carbamates cooperatively catalyzed by TpCu, where Tp = (hydrotris(4,5-bromopyrazolyl)borate), and a chiral spiro phosphoric acid. These reactions provide straightforward access to unnatural optically active N-carbonate α-alkyl-α-amino esters, which are widely used in artificial peptide synthesis. Relevant achievements were published in ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 21, 13143–13148. DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.2c03937.