Lanostanes, a large family of tetracyclic triterpenoids derived from lanosterol, have a diverse array of structures and a variety of bioactivities, including antitumor, anti-HIV, and anti-inflammatory activities. The anti-inflammatory activity of some lanostanes arises from their ability to mediate the inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and COX-2 expression by regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Recently, Jun Deng 's research group used the Bioinspired Structure Network Analysis method to analyze the bio-source of spirochenside A and proposed a possible source synthesis approach for spirochenside A (Figure 1). The authors believe that wool sterol (4) is firstly oxidized selectively at C17 position by a series of enzymes, followed by epoxidation of tetra-substituted double bonds, followed by two steps of Wagner-Meerwein methyl migration and rearrangement to form the key intermediate 10 and Meinwald rearrangement to obtain the 6/5/6/5 four ring skeleton and finally Spirochensilides A is obtained by further closing the spiro ketal ring. Within 17 steps, the efficient biomimetic transformation from cheap and easily available lanosterol to spirochenside A was realized, which provided clues for the analysis and efficient synthesis of this kind of natural possible biosynthetic pathway. Relevant achievements were published in J. Am. Chem. Soc., DOI:10.1021/jacs.2c07198
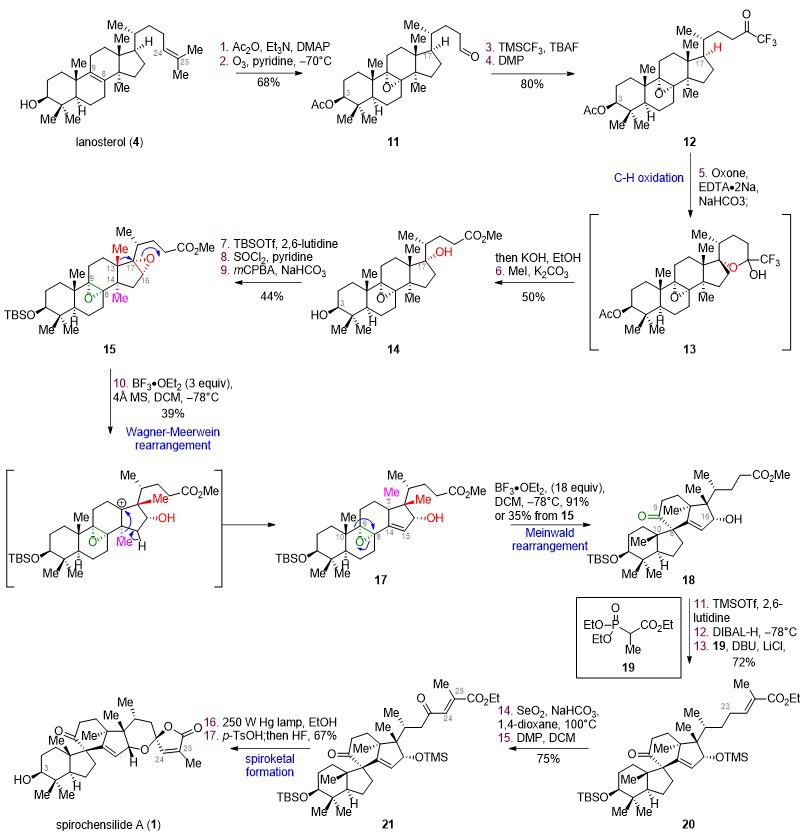
Figure 1. Biomimetic Synthesis of Spirochensilide A