In 2010, the Heck reaction gained renewed attention following the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. As a fundamental method for constructing C(sp²)–C(sp²) bonds, it has been widely applied in industrial processes and pharmaceutical synthesis. Recently, asymmetric reductive Heck reactions enabling C(sp³)–C(sp²) bond formation have emerged as an important and rapidly developing area in organic synthesis. Nevertheless, achieving highly efficient asymmetric reductive Heck reactions with common olefins remains challenging. Existing methods are often limited by narrow substrate scope, difficulties in balancing regio- and enantioselectivity, and a strong reliance on highly reactive aryl electrophiles such as aryl iodides or triflates. Although aryl bromides and chlorides are more economical and readily available, their inert C–Br and C–Cl bonds have largely impeded their application. Therefore, the development of asymmetric reductive Heck reactions between inexpensive aryl halides and olefins remains a significant challenge.
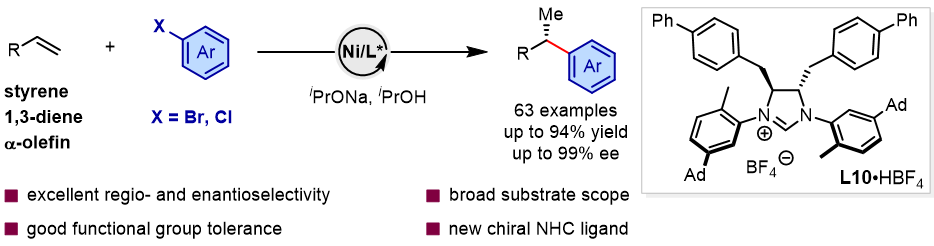
Figure 1. Nickel-catalyzed enantioselective reductive Heck reaction of olefins with aryl bromides and chlorides.
To address this challenge, Li-Jun Xiao and co-workers at Nankai University recently designed and synthesized a series of novel chiral dihydroimidazolium-derived N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands. By introducing remote, bulky substituents onto the aryl backbone of the ligand, a “narrow and deep” chiral pocket was created, enabling a nickel-catalyzed enantioselective reductive Heck reaction of olefins with aryl bromides and chlorides (Figure 1). Benefiting from this newly developed ligand framework, the catalytic system markedly enhances the activation of C–Br and C–Cl bonds, effectively suppresses β-hydride elimination and other side reactions, and simultaneously achieves high regio- and enantioselectivity. This method is compatible with a broad range of olefins, including styrenes, 1,3-dienes, and aliphatic alkenes, as well as diverse (hetero)aryl bromides and chlorides, delivering products with excellent chemoselectivity, regioselectivity, and enantioselectivity, thereby demonstrating significant potential for practical applications. Relevant achievements were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2026, DOI: 10.1002/anie.202525600.