Carbohydrates play a central role in many biological processes and have important applications in modern therapeutic developments. O- and N-glycosides bearing oxygen and nitrogen linkers, respectively, at the anomeric position are the two most prevalent classes of carbohydrate. Compared with divalent oxygen atoms, trivalent nitrogen atoms can adopt more diverse bonding patterns and their reactivities can be more strongly influenced by steric and electronic factors. The versatile bonding abilities of nitrogen endow N-glycosides with rich structural features that enable their varied biological functions. However, the distinct chemical properties of various nitrogen motifs, especially their basicity, also pose a considerable challenge in regard to the synthesis of N-glycosides.
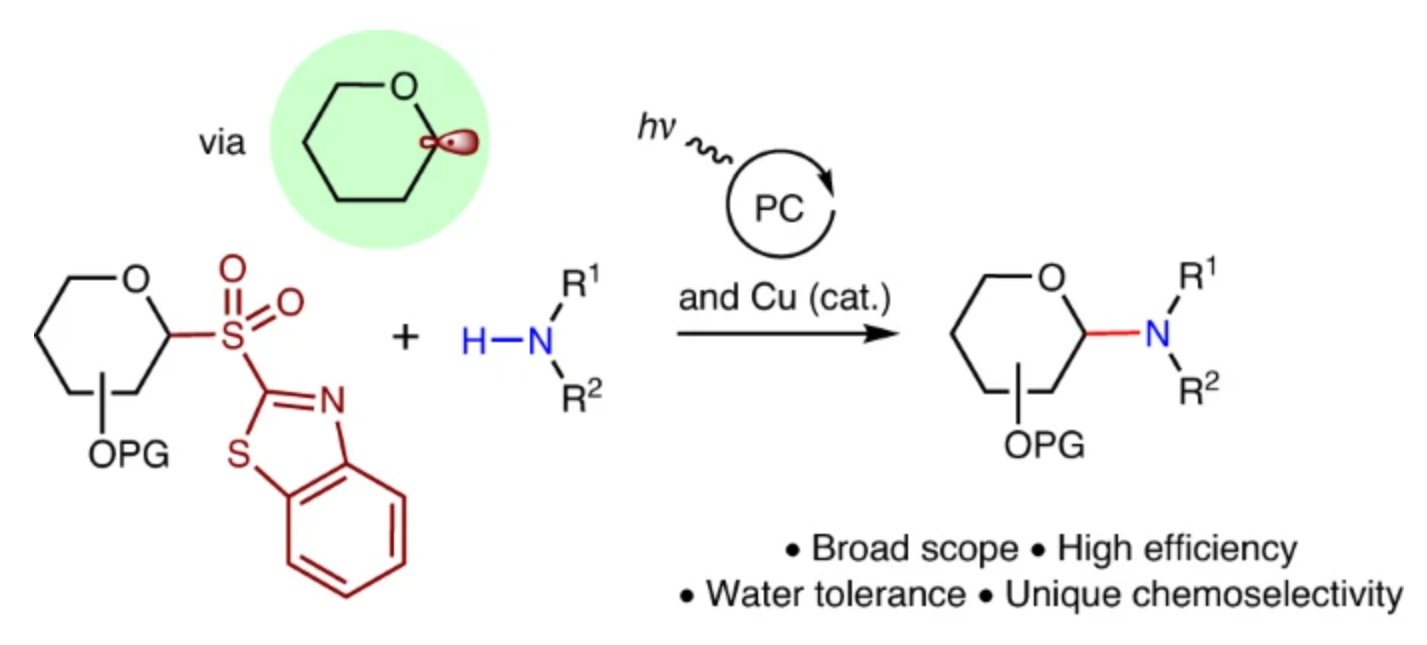
Recently, Gong Chen’s group working together with Ming Joo Koh of National University of Singapore have have developed a glycosyl radical-mediated N-glycosylation reaction under combined copper and photoredox catalysis. The identification of readily reducible benzothiazolyl sulfones as glycosyl donors was the key to achieving radical N-glycosylation reactivity with N-nucleophiles under regular photoinduced, Cu-catalysed conditions. The addition of an appropriate photocatalyst provided an electron shuttle to facilitate more efficient SET activation of the sulfone donor, which greatly accelerated the N-glycosylation process. The catalytic method was successfully applied in the preparation of a variety of complex N-glycosides such as nucleosides and their analogues from readily accessible precursors. Of particular note, this radical N-glycosylation protocol exhibits high chemoselectivity and water tolerance, effectively overcoming the inherent problems associated with traditional cationic glycosylations. They expect this work to further encourage the development of glycosyl radical-mediated cross-coupling reactions with other heteroatomic reagents in the assembly of a broader array of medicinally valuable carbohydrates that are difficult to access by other means. Relevant achievements were published in Nat. Synth., 2024, DOI: s44160-024-00496-7.