
Organosilicon compounds have been widely used in synthetic chemistry, material science, and medicinal chemistry. Catalytic selective hydrosilylation of alkenes and alkyne derivatives represent the most important and versatile protocol for the synthesis of organosilanes. Methylenecyclopropanes (MCPs), featuring a highly strained cyclopropane ring with an exocyclic C═C double bond, have emerged as versatile building blocks in synthetic chemistry. However, catalytic hydrosilylation of MCPs has met with very limited successes. So far, only few examples of metal-catalyzed hydrosilylation of MCPs have been reported. These transition-metal-catalyzed reactions afforded either (cyclopropyl)methylsilanes or homoallylsilanes by 2,1-hydrosilylation or hydrosilylation followed by cyclopropane ring-opening. Furthermore, the catalytic reactions suffered from very limited substrate scopes and relatively poor chemo- and stereoselectivity. To the best of our knowledge, the efficient and selective catalytic hydrosilylation of MCPs affording silacycles has not been reported. On the other hand, rare-earth (RE) complex-catalyzed hydrosilylation reactions have emerged as powerful synthetic method because of their unique reactivity and selectivity.
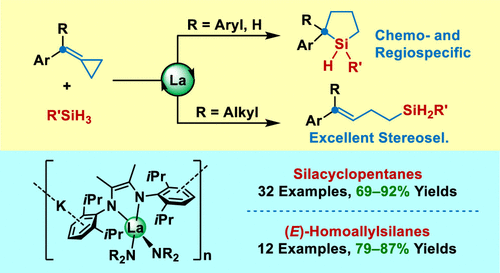
Recently, Jianfeng Li & Chunming Cui’s group have disclosed that lanthanum ate complex 1 enabled highly efficient hydrosilylations of aryl MCPs with various primary silanes. Silacyclopentanes and (E)-homoallylsilanes could be obtained selectively in high yields for 1-aryl and 1,1-diaryl as well as 1-aryl-1-aklyl-substituted MCPs, respectively. The experimental and theoretical studies disclosed the cascade inter- and intramolecular mechanisms for the formation of silacyclopentanes. The intramolecular hydrosilylation of homoallylsilanes could be achieved only with the La hydride catalyst featuring a large ionic size metal. As far as they know, no RE-metal complexes have been reported to efficiently catalyze similar intramolecular hydrosilylation reactions. This work demonstrated the significant roles of a large lanthanum ion for the high reactivity and excellent selectivity. They are continuing to investigate the applications of this family of catalysts in insertion reactions. Relevant achievements were published in J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c12355.