Oxidation of alkenes is one of the most fundamental chemical transformations, not only because alkenes are feedstock chemicals that are readily available from petroleum and biomass, but also because such oxidations provide convenient and economical routes to oxygen-enriched molecules such as epoxides, 1,2-diols and carbonyls, which are prevalent in numerous natural products, pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Widely-used oxidants for alkene oxidation are metal oxides such as OsO4 and KMnO4, yielding desired oxygen-enriched products but with stoichiometric metallic waste. To eliminate metallic waste towards achieving greener oxidation methods, non-metal oxidants such as ozone (O3) and its surrogates, photoexcited nitroarenes, have received constantly growing interest during the past decades.
Recently, Mengchun Ye’s group have developed a photoexcited nitroarene-enabled carbon chain-elongated oxidation of alkenes via tandem oxidative cleavage and dipolar cycloaddition, wherein the alkene first undergoes oxidative cleavage to form a key carbonyl imine dipole that is captured by the alkene itself to give the final carbon chain-elongated oxidative product. The use of proper alkenes such as enol ether or styrene and derivatives proves critical to the reactivity, and a wide range of isoxazolidines can be obtained in up to 92% yield with high regioselectivity. The reaction demonstrates that the development of versatile transformations beyond ozonolysis and dihydroxylation for ozone or photoexcited nitroarene-enabled oxidation of alkenes is feasible. Relevant achievements were published in Nat. Commun., 2025. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59274-4.
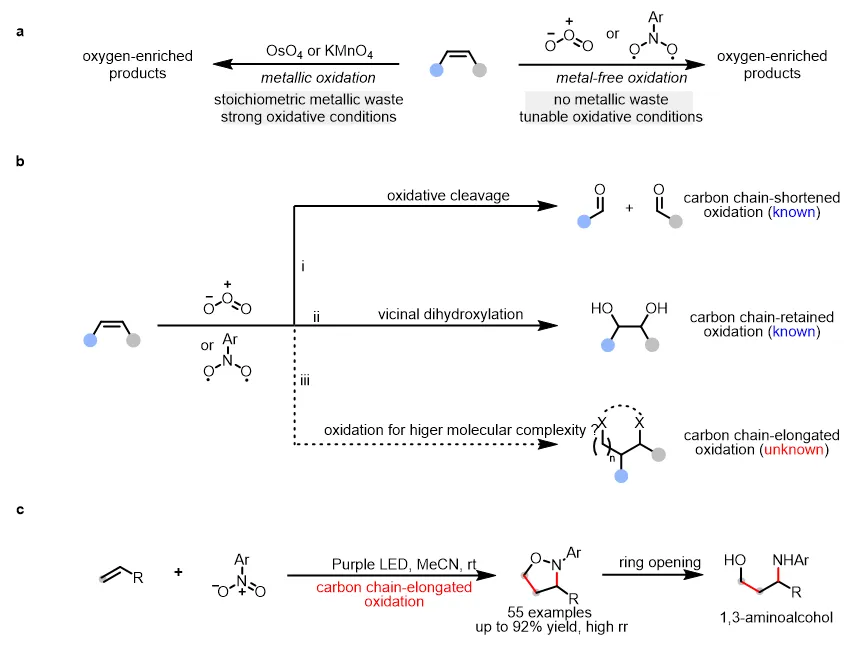
图1. 臭氧或光激发硝基芳烃氧化烯烃
反应以乙腈为溶剂,在385-390 nm波长、8W功率的LED灯照射下,在氮气氛围中进行,获得高达92%的收率。实验表明,硝基芳烃底物的官能团容忍性较好,能够耐受氟、氯、溴、氰基、三氟甲基和硝基等各种基团。此外,硝基杂芳烃底物如硝基吡啶和硝基嘧啶可以40–72%的收率得到相应的目标产物。作者尝试了一系列含有单取代基烯烃(如线性烷基、支链烷基、位阻较大的烷基、含氧官能团的烷基、芳基等)以及1,1-二取代烯烃,各种烯烃底物均能顺利参与反应,生成目标产物。
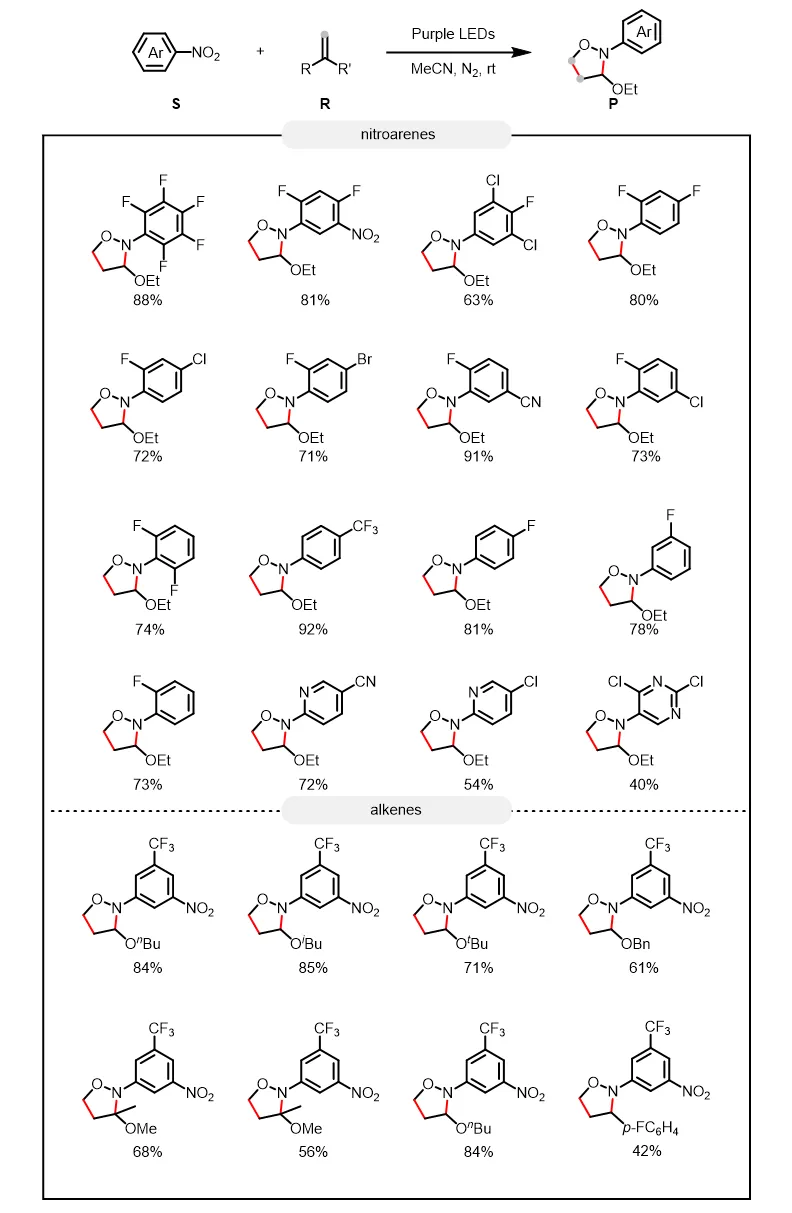
图2. 硝基芳烃及烯烃底物拓展
为展示方法的实用性,作者进行了放大实验(图3a)。此外,为了考察反应的实用性,作者进行了产物转化实验。含乙氧基的异噁唑烷P1与BF3·Et2O反应后生成一种活性亚胺中间体,该中间体可与各种亲核试剂反应生成相应的目标产物(图3b);异噁唑烷还可被还原开环生成相应的1,3-氨基醇(图3c)。为了探究反应机理,作者进行了相关的机理实验。体系中加入自由基捕获剂TEMPO及DMPO时无目标产物生成,证明反应可能涉及自由基过程(图3d);光“开-关”实验证实了连续照射氧化的必要性(图3e);当使用空间位阻较大的内烯作为底物时,意外观察到产物P60而不是相应的异噁唑烷(图3f),作者推测P60来自两个羰基亚胺中间体的环化,该中间体无法与大位阻内烯进行环加成反应;在标准条件下观察到的醛P61的形成,表明了反应涉及到臭氧中间体介导的烯烃裂解途径(图3g);基于以上实验结果和以往研究,作者提出了一种可能的反应机理:硝基芳烃的光激发和随后的系统间交叉(ISC)形成双自由基中间体,然后与烯烃进行自由基加成,形成不稳定的五元环中间体I。中间体I的裂解产生了重要的羰基亚胺中间体II以及副产物醛。最后,中间体II被烯烃捕获,生成所需的异噁唑烷产物(图3h)。
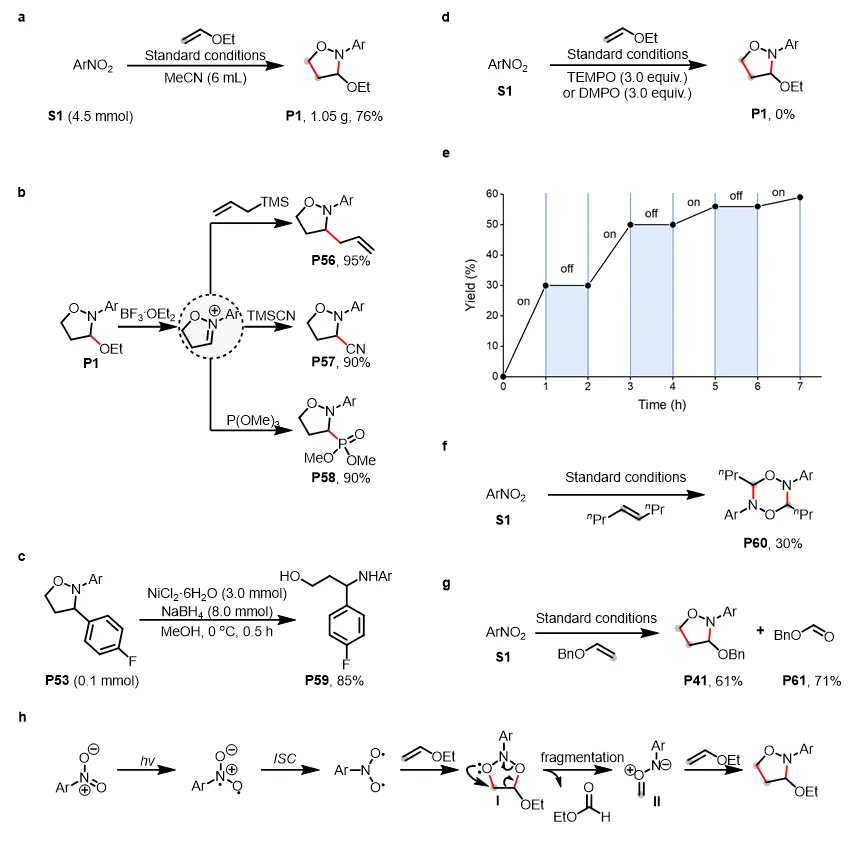
图3. 产物应用与反应机理
综上所述,作者通过串联氧化裂解和偶极环加成开发了光激发的硝基芳烃使烯烃碳链延长的氧化反应。其中烯烃首先经历氧化裂解,形成关键的羰基亚胺偶极子,其被烯烃本身捕获,得到碳链延长的氧化产物。使用合适的烯烃如烯醇醚或苯乙烯及其衍生物证明对反应性至关重要,并且可以以高达92%的产率和高区域选择性获得各种异噁唑烷。该反应表明,除了臭氧分解和双羟基化外,臭氧或光激发硝基芳烃氧化烯烃的多用途转化是可行的。
原文(扫描或长按二维码,识别后直达原文页面):

Photoexcited nitroarene-enabled carbon chain-elongated oxidation of alkenes via tandem oxidative cleavage and dipolar cycloaddition
Xuqiang Guo, Xinwen Cui, Mingzhen Lu, Qi-Lin Zhou, Weiwei Xu & Mengchun Ye
Nat. Commun., 2025, 16, 4504, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59274-4