Multiple-bonded silicon compounds and their congeners play important roles as synthetic reagents for the construction of complex organosilanes and activation of small molecules with distinctive reaction patterns. In particular, disilynes(RSi≡SiR) have been shown to exhibit diverse reaction patterns in the activation of small molecules and organic substrates. Disilynes are homologues of alkynes, but their structures are in trans-bent configurations, unlike the linear structures of alkynes. Numerous theoretical calculations have shown that the structure of disilynes is largely related to the substituent group, which enables effective modulation of their properties and reactivity through the substituent group. Due to the unsaturated bonding of disilynes, it is foreseen that they can be used as basic synthons for the construction of organosilicon compounds. However, so far, the study of its reaction pattern is still relatively deficient, especially with organic functional groups and small molecules, which still need to be further explored.
Recently, Chunming Cui’s group have described the reactions of NHB-stabilized disilyne (NHB)Si≡Si(NHB) (1, NHB = [ArN(CMe)2NAr]B, Ar = 2,6-iPr2C6H3) with internal alkynes. Reaction of disilyne 1 with one equivalent of bis(trimethylsilyl)acetylene led to a reversible [1 + 2] cycloaddition of one of the Si atoms with the alkyne and the insertion of the other Si into one of Ar rings with the formation of a silirenyl–silepin 2, whereas reaction of 1 with two equivalents of Me3SiCCSiMe3 resulted in the formal addition of the Csp–Si bond to the Si≡Si triple bond to give disilene (NHB)(Me3Si)Si=Si(CCSiMe3)(NHB). Reaction of 1 with 1,3-diyne Me3SiCCCCSiMe3 yielded a 1,2-disilacyclobut-3-ene via cycloaddition, ring expansion, and NHB 1,2-shift sequence. The initial [1 + 2] cycloaddition of one of the silicon atoms with an alkyne was strongly supported by DFT calculations. The results demonstrated the significant bis(silylene) character and rich synthetic potential of bis(boryl) disilyne 1. The results indicated that disilyne could be a powerful reagent for the synthesis of novel silicon heterocycles. Relevant achievements were published in J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c05436.
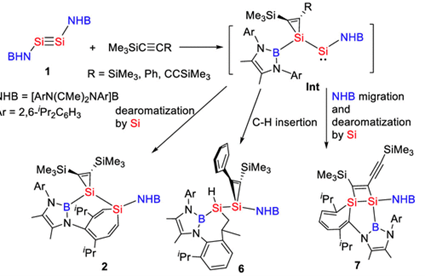
Reaction of a Disilyne with Internal Alkynes: Reversible [1 + 2] Cycloaddition and Formation of Strained Unsaturated Silacycles
Yazhou Ding, Wen Jin, Jianying Zhang, and Chunming Cui*
J. Am. Chem. Soc ., 2024, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c05436